C#, Xamarin 및 SkiaSharp를 사용하여 즐거움과 놀라움(플랫폼 간)
크로스 플랫폼 개발은 특히 모바일 플랫폼이 관련된 경우 까다로울 수 있습니다. 플랫폼별로 별도의 앱을 구축하여 완전히 피할 수 있지만 비용 효율적이지도 않고 특별히 재미있지도 않습니다.
What is SkiaSharp?
Xamarin와 같은 도구는 적어도 모든 중요한 플랫폼에서 공통 프로그래밍 언어를 사용하는 데 도움이 되지만, 응용 프로그램의 비즈니스 논리를 공유하는 데는 유용하지만 UI 논리를 자동으로 쉽게 공유할 수 있는 것은 아닙니다.
Xamarin /Microsoft는 여러 플랫폼에서 UI 구현을 공유하는 데 도움이 되는 여러 도구를 제공합니다. 그들은 창조했습니다 Xamarin. 양식 애플리케이션에 대한 UI 보기를 추상적으로 한 번 정의한 다음 지원되는 플랫폼에서 다시 사용할 수 있습니다. Xamarin. Forms는 아주 멋지다, 적어도 우리는 그렇게 생각하기 때문에 신제품 당신이 할 수 있는지 확인하기 위해 사용 가능 더 멋진 것들 Xamarin와 함께 . 양식. 하지만 Forms가 할 수 없지만 여전히 필요한 작업이 여전히 있다면 어떨까요? C#의 여러 플랫폼에서 사용자 지정 그래픽을 렌더링하는 것이 좋지 않을까요?
글쎄요, 몇 년 전만 해도 이 작업을 하고 싶었지만 당시에는 모든 중요한 플랫폼에서 사용할 수 있는 크로스 플랫폼 C# 2D API가 없다는 것이 문제였습니다. 그래서 다양한 네이티브 2D 렌더링 API에 대한 추상화를 만들어 일부 렌더링 로직을 한 번 작성하고 일부 추상화 레이어가 다양한 기본 렌더링 API에 대한 올바른 호출 순서로 변환하도록 했습니다. 그러나 내가 발견 한 것은이 경로를 사용하여 많은 흥미로운 오버 헤드가 있다는 것입니다. 내 논리는 C #에서 2D 그래픽 프리미티브를 빌드 한 다음 Android에서 Java 객체로 표현해야하는 다음 이러한 Java 객체를 Android의 기본 렌더링 계층에서 네이티브 클래스로 표현해야하며 각 플랫폼에 대해 다음과 같이 표현해야합니다. 이렇게 많은 추상화 계층을 갖는 것은 2D 렌더링 API와 복잡한 2D 그래픽을 사용하는 수다스러움과 결합될 때 적지 않은 오버헤드를 유발했습니다.
글쎄요, Xamarin 자신도 이와 같은 고통을 느꼈을 것입니다. SkiaSharp은 Xamarin를 통해 Android/iOS 플랫폼을 비롯한 다양한 플랫폼에서 사용할 수 있는 크로스 플랫폼 2D 그래픽 렌더링 API입니다. SkiaSharp은 Skia 렌더링 라이브러리에 대한 C 네이티브 API를 직접 둘러싼 일부 C# 바인딩입니다. Skia는 Android와 Chrome 브라우저 및 기타 수많은 유명 프로젝트에서 많이 사용되는 빠른 오픈 소스 렌더링 라이브러리입니다. SkiaSharp을 사용하면 C# API가 Skia 네이티브 라이브러리와 직접 통신할 수 있으므로 API와의 상호 작용에서 비교적 적은 오버헤드로 많은 플랫폼에서 빠른 2D 그래픽 렌더링을 수행할 수 있습니다. 이 기사에서는 API를 시작하는 방법을 안내합니다.
시작하기
먼저 Visual Studio를 열고 새 플랫폼 간 프로젝트를 만듭니다. Xamarin Visual Studio에 설치할 수 있는 템플릿 중 하나입니다.
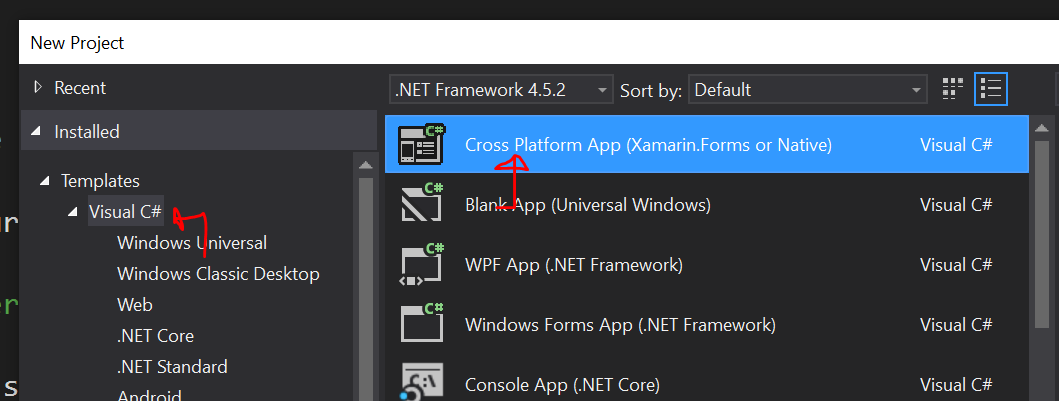
기본 설정에 따라 Xamarin.Forms 앱 또는 네이티브 앱으로 만들 수 있습니다. 이 데모를 위해 공유 프로젝트가 아닌 PCL (이식 가능한 클래스 라이브러리)을 통해 코드를 공유하는 기본 앱을 만들었습니다. 이렇게 하면 템플릿과 연결된 기본 플랫폼 호스트가 만들어지며 필요에 따라 SkiaSharp도 지원하는 경우 추가 프로젝트를 추가할 수 있습니다.
네이티브 플랫폼 간 앱을 선택하면 플랫폼, Xamarin.Android 프로젝트 및 Xamarin.iOS 프로젝트 간에 코드를 공유하는 PCL 프로젝트가 만들어졌지만, 두 플랫폼 모두 렌더링을 위해 SkiaSharp을 지원하기 때문에 WPF 프로젝트와 UWP 프로젝트도 믹스에 추가했습니다. 그런 다음 솔루션에 추가 한 두 개의 새 프로젝트에 PCL 프로젝트에 대한 참조를 추가했습니다.
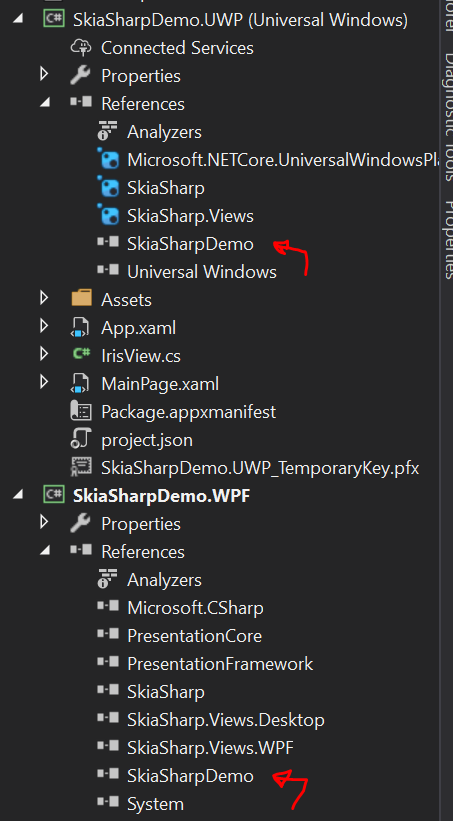
다음으로, 솔루션에 몇 가지 NuGet 패키지를 추가해야 합니다. 솔루션 노드를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭하고 "솔루션에 대한 Nuget 패키지 관리"를 선택하면 솔루션의 모든 프로젝트에 SkiaSharp 및 SkiaSharp.Views를 온라인으로 검색하여 설치할 수 있습니다. SkiaSharp.Views에는 선택한 플랫폼에서 SkiaSharp의 렌더링을 네이티브 UI 보기로 부트스트랩하여 몇 가지 상용구 논리를 절약하는 데 도움이 되는 몇 가지 도우미 클래스가 있습니다. SkiaSharp.Views 는 특정 UI 플랫폼에 바인딩되지 않기 때문에 유틸리티를 제공하지 않는 PCL을 제외한 모든 프로젝트에 대해 설치해야 합니다.
우리의 목표
간단한 원을 렌더링하여 간단한 것으로 시작하지만 훨씬 더 복잡한 것으로 이동할 것입니다. 이전 샘플 브라우저 중 하나에는 깔끔한 애니메이션 홍채 효과가 있습니다.

이 작업은 많은 이미지를 오버레이한 다음 다른 방향으로 회전시키는 방식으로 수행되었습니다. 이 경우 이미지는 정적이었지만 모든 논리를 뷰에 넣고 모든 것을 동적으로 렌더링 할 수 있는지 궁금했습니다. 그 목표를 향해 나아갑시다.
먼저 SkiaSharp.Views를 활용하여 Android용 IrisView 라는 구성 요소를 만듭니다. 나중에 이를 더 확장한 다음 다른 플랫폼에 대한 세부 정보를 채울 것입니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Android.App;
using Android.Content;
using Android.OS;
using Android.Runtime;
using Android.Views;
using Android.Widget;
using SkiaSharp;
using Android.Util;
namespace SkiaSharpDemo.Droid
{
public class IrisView
: SkiaSharp.Views.Android.SKCanvasView
{
private Handler _handler;
private void Initialize()
{
_handler = new Handler(Context.MainLooper);
}
public IrisView(Context context)
: base(context)
{
Initialize();
}
public IrisView(Context context, IAttributeSet attrs)
: base(context, attrs)
{
Initialize();
}
public IrisView(Context context, IAttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr)
: base(context, attrs)
{
Initialize();
}
protected IrisView(IntPtr javaReference, JniHandleOwnership transfer)
: base(javaReference, transfer)
{
Initialize();
}
protected override void OnDraw(SKSurface surface, SKImageInfo info)
{
base.OnDraw(surface, info);
//Get the canvas from the skia surface.
var context = surface.Canvas;
//Clear out the current content for the canvas.
context.DrawColor(SKColors.Transparent, SKBlendMode.Clear);
//Determine the center for the circle.
var centerX = info.Width / 2.0f;
var centerY = info.Height / 2.0f;
//Determine the radius for the circle.
var rad = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height) / 2.0f;
//Create the paint object to fill the circle.
using (SKPaint p = new SKPaint())
{
p.IsStroke = false;
p.IsAntialias = true;
p.Color = new SKColor(255, 0, 0);
//Fill the circle.
context.DrawCircle(centerX, centerY, rad, p);
};
}
}
}
이 코드의 대부분은 일반 Android 보기 내에서 SkiaSharp을 사용하여 콘텐츠를 렌더링할 수 있도록 SkiaSharp.Views 제공하는 보기 중 하나를 확장하는 상용구 논리입니다. 페인팅을 수행하는 논리에 초점을 맞추면 :
//Get the canvas from the skia surface.
var context = surface.Canvas;
//Clear out the current content for the canvas.
context.DrawColor(SKColors.Transparent, SKBlendMode.Clear);
//Determine the center for the circle.
var centerX = info.Width / 2.0f;
var centerY = info.Height / 2.0f;
//Determine the radius for the circle.
var rad = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height) / 2.0f;
//Create the paint object to fill the circle.
using (SKPaint p = new SKPaint())
{
p.IsStroke = false;
p.IsAntialias = true;
p.Color = new SKColor(255, 0, 0);
//Fill the circle.
context.DrawCircle(centerX, centerY, rad, p);
};
여기 우리가:
- 칠할 Skia Canvas를 획득하세요.
- 캔버스에 표시된 초기 색상을 지웁니다(이전 렌더링을 지웁니다).
- 뷰의 중심과 뷰에 그릴 수 있는 원의 반지름을 결정합니다.
- 안티 앨리어싱을 사용하여 빨간색으로 채워지는 Skia Paint 오브젝트를 만듭니다.
- 구성된 페인트 개체를 사용하여 캔버스에 원을 그립니다.
그런 다음 기본 활동으로 돌아가서 이 IrisView를 레이아웃에 추가하면 다음과 같은 내용이 표시됩니다.

좋아, 이것은 깔끔하지만 분명히 렌더링 로직이 기본 Android 뷰에 있다면 플랫폼 간에 공유할 수 없습니다. 이제 이것을 조금 리팩토링해 보겠습니다. PCL에서 다음 내용으로 IrisRenderer.cs 라는 클래스를 만듭니다.
using SkiaSharp;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SkiaSharpDemo
{
public class IrisRenderer
{
public IrisRenderer()
{
}
private DateTime _lastRender = DateTime.Now;
private bool _forward = true;
private double _progress = 0;
private double _duration = 5000;
private Random _rand = new Random();
private static double Cubic(double p)
{
return p * p * p;
}
public static double CubicEase(double t)
{
if (t < .5)
{
var fastTime = t * 2.0;
return .5 * Cubic(fastTime);
}
var outFastTime = (1.0 - t) * 2.0;
var y = 1.0 - Cubic(outFastTime);
return .5 * y + .5;
}
private bool _first = true;
public void RenderIris(SKSurface surface, SKImageInfo info)
{
if (_first)
{
_first = false;
_lastRender = DateTime.Now;
}
var currTime = DateTime.Now;
var elapsed = (currTime - _lastRender).TotalMilliseconds;
_lastRender = currTime;
if (_forward)
{
_progress += elapsed / _duration;
}
else
{
_progress -= elapsed / _duration;
}
if (_progress > 1.0)
{
_progress = 1.0;
_forward = false;
_duration = 1000 + 4000 * _rand.NextDouble();
}
if (_progress < 0)
{
_progress = 0;
_forward = true;
_duration = 1000 + 4000 * _rand.NextDouble();
}
var context = surface.Canvas;
context.DrawColor(SKColors.Transparent, SKBlendMode.Clear);
//Determine the center for the circle.
var centerX = info.Width / 2.0f;
var centerY = info.Height / 2.0f;
//Determine the radius for the circle.
var rad = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height) / 2.0f;
var fromR = 255;
var fromG = 0;
var fromB = 0;
var toR = 0;
var toG = 0;
var toB = 255;
var actualProgress = CubicEase(_progress);
var actualR = (byte)Math.Round(fromR + (double)(toR - fromR) * actualProgress);
var actualG = (byte)Math.Round(fromG + (double)(toG - fromG) * actualProgress);
var actualB = (byte)Math.Round(fromB + (double)(toB - fromB) * actualProgress);
//Create the paint object to fill the circle.
using (SKPaint p = new SKPaint())
{
p.IsStroke = false;
p.IsAntialias = true;
p.Color = new SKColor(actualR, actualG, actualB);
//Fill the circle.
context.DrawCircle(centerX, centerY, rad, p);
};
}
}
}
그리고 Android용 IrisView를 다음과 같이 수정합니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Android.App;
using Android.Content;
using Android.OS;
using Android.Runtime;
using Android.Views;
using Android.Widget;
using SkiaSharp;
using Android.Util;
namespace SkiaSharpDemo.Droid
{
public class IrisView
: SkiaSharp.Views.Android.SKCanvasView
{
private IrisRenderer _irisRenderer;
private Handler _handler;
private void Initialize()
{
//The IrisRenderer will perform the actual rendering logic for this view.
_irisRenderer = new IrisRenderer();
_handler = new Handler(Context.MainLooper);
//This starts a tick loop that we will use later for animation.
_handler.Post(Tick);
}
private DateTime _lastTime = DateTime.Now;
private void Tick()
{
DateTime currTime = DateTime.Now;
//Don't render new frames too often.
if (currTime - _lastTime < TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(16))
{
_handler.Post(Tick);
return;
}
_lastTime = currTime;
Invalidate();
_handler.Post(Tick);
}
public IrisView(Context context)
: base(context)
{
Initialize();
}
public IrisView(Context context, IAttributeSet attrs)
: base(context, attrs)
{
Initialize();
}
public IrisView(Context context, IAttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr)
: base(context, attrs)
{
Initialize();
}
protected IrisView(IntPtr javaReference, JniHandleOwnership transfer)
: base(javaReference, transfer)
{
Initialize();
}
protected override void OnDraw(SKSurface surface, SKImageInfo info)
{
base.OnDraw(surface, info);
_irisRenderer.RenderIris(surface, info);
}
}
}
이러한 방식으로 모든 렌더링 로직을 PCL에 있는 공유 클래스로 팩터링했으며, 이는 우리가 목표로 삼고자 하는 모든 플랫폼 간에 공유할 수 있습니다. 한 번만 코딩하면 완료됩니다. 또한 렌더러가 경과 시간을 분석하고 선형 보간을 사용하여 변경 사항을 애니메이션화할 수 있도록 일정 간격으로 뷰를 계속 무효화하는 기본 애니메이션 시스템을 추가했습니다(3차 여유 기능으로 완화됨). 꽤 멋지지 않나요? 다음은 파란색과 빨간색 사이의 애니메이션 중에 원이 어떻게 보이는지입니다.

자, 이제 IrisView에 대한 나머지 구현을 채울 수 있습니다. 각 플랫폼마다 UI 뷰를 구성하는 요소에 대한 요구 사항이 다르고 애니메이션 루프를 구동하는 데 사용할 수 있는 메커니즘이 다르기 때문에 별도의 클래스여야 하지만, 아이디어는 이러한 클래스의 콘텐츠를 최소화하여 플랫폼 특정 동작만 포함하는 것입니다. 또한 이러한 클래스의 논리를 더욱 줄일 수 있는 추가 추상화(예: 애니메이션과 관련된 추상화)를 구축할 수 있는 옵션이 있습니다. iOS용 뷰의 버전은 다음과 같습니다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Foundation;
using SkiaSharp;
using UIKit;
using CoreGraphics;
using CoreFoundation;
namespace SkiaSharpDemo.iOS
{
public class IrisView
: SkiaSharp.Views.iOS.SKCanvasView
{
private IrisRenderer _irisRenderer;
public IrisView()
: base()
{
Initialize();
}
public IrisView(CGRect frame)
: base(frame)
{
Initialize();
}
public IrisView(IntPtr p)
: base(p)
{
Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
BackgroundColor = UIColor.Clear;
_irisRenderer = new IrisRenderer();
DispatchQueue.MainQueue.DispatchAsync(Tick);
}
private DateTime _lastTime = DateTime.Now;
private void Tick()
{
DateTime currTime = DateTime.Now;
if (currTime - _lastTime < TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(16))
{
DispatchQueue.MainQueue.DispatchAsync(Tick);
return;
}
_lastTime = currTime;
SetNeedsDisplay();
DispatchQueue.MainQueue.DispatchAsync(Tick);
}
public override void DrawInSurface(SKSurface surface, SKImageInfo info)
{
base.DrawInSurface(surface, info);
var ctx = UIGraphics.GetCurrentContext();
ctx.ClearRect(Bounds);
_irisRenderer.RenderIris(surface, info);
}
}
}
그리고 WPF :
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using SkiaSharp.Views.Desktop;
namespace SkiaSharpDemo.WPF
{
public class IrisView
: SkiaSharp.Views.WPF.SKElement
{
private IrisRenderer _irisRenderer;
public IrisView()
{
Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
_irisRenderer = new IrisRenderer();
Task.Delay(8).ContinueWith((t) => Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.Normal, (Action)Tick));
}
private DateTime _lastTime = DateTime.Now;
private void Tick()
{
DateTime currTime = DateTime.Now;
if (currTime - _lastTime < TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(16))
{
Task.Delay(8).ContinueWith((t) => Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.Normal, (Action)Tick));
return;
}
_lastTime = currTime;
InvalidateVisual();
Task.Delay(8).ContinueWith((t) => Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.Normal, (Action)Tick));
}
protected override void OnPaintSurface(SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs e)
{
base.OnPaintSurface(e);
_irisRenderer.RenderIris(e.Surface, e.Info);
}
}
}
And UWP:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using Windows.UI.Core;
using SkiaSharp.Views.UWP;
namespace SkiaSharpDemo.UWP
{
public class IrisView
: SkiaSharp.Views.UWP.SKXamlCanvas
{
private IrisRenderer _irisRenderer;
public IrisView()
{
Initialize();
}
private void Initialize()
{
_irisRenderer = new IrisRenderer();
Task.Delay(8).ContinueWith((t) => Dispatcher.RunAsync(CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, Tick));
}
private DateTime _lastTime = DateTime.Now;
private void Tick()
{
DateTime currTime = DateTime.Now;
if (currTime - _lastTime < TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(16))
{
Task.Delay(8).ContinueWith((t) => Dispatcher.RunAsync(CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, Tick));
return;
}
_lastTime = currTime;
Invalidate();
Task.Delay(8).ContinueWith((t) => Dispatcher.RunAsync(CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, Tick));
}
protected override void OnPaintSurface(SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs e)
{
base.OnPaintSurface(e);
_irisRenderer.RenderIris(e.Surface, e.Info);
}
}
}
이제 이들 각각을 실행하고 정확히 동일한 렌더링 동작을 관찰할 수 있습니다! 이것이 왜 그렇게 대단한지 아직 이해하지 못한다면 상황을 훨씬 더 복잡하게 만들어 볼까요? 다음 콘텐츠로 IrisRenderer를 업데이트합니다.
using SkiaSharp;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace SkiaSharpDemo
{
public class IrisArc
{
public float CenterX { get; set; }
public float CenterY { get; set; }
public bool AreCogsOutward { get; set; }
public int NumLevels { get; set; }
public float BaseHue { get; set; }
public float BaseLightness { get; set; }
public float BaseSaturation { get; set; }
public float Radius { get; set; }
public float Span { get; set; }
public List<Tuple<float, int>> Shape { get; set; }
public float MinTransitionLength { get; set; }
public float MaxTransitionLength { get; set; }
public float RotationAngle { get; set; }
public float Opacity { get; set; }
public bool IsClockwise { get; internal set; }
public IrisArc()
{
CenterX = .5f;
CenterY = .5f;
AreCogsOutward = true;
NumLevels = 3;
BaseHue = 220;
BaseLightness = 50;
BaseSaturation = 50;
Radius = .75f;
Span = .2f;
Shape = new List<Tuple<float, int>>();
MinTransitionLength = 6;
MaxTransitionLength = 10;
RotationAngle = 0;
Opacity = .8f;
GenerateShape();
}
private static Random _rand = new Random();
private void GenerateShape()
{
float currentAngle = 0.0f;
int currentLevel = 1 + (int)Math.Round(_rand.NextDouble() * this.NumLevels);
float degreeChange = 0.0f;
while (currentAngle <= 360)
{
AddToShape(currentAngle, currentLevel);
if (currentAngle >= 360)
{
break;
}
degreeChange = (float)Math.Round(MinTransitionLength + _rand.NextDouble() *
MaxTransitionLength);
if (currentAngle + degreeChange > 360)
{
degreeChange = 360 - currentAngle;
}
currentAngle = currentAngle + degreeChange;
}
}
private void AddToShape(float currentAngle, int currentLevel)
{
bool isUp = true;
int changeAmount;
int maxLevels = NumLevels + 1;
if (currentLevel == maxLevels)
{
isUp = false;
}
else
{
if (_rand.NextDouble() > .5)
{
isUp = false;
}
}
if (isUp)
{
changeAmount = (int)Math.Round(1.0 + _rand.NextDouble() * (maxLevels - currentLevel));
currentLevel = currentLevel + changeAmount;
if (currentLevel > this.NumLevels)
{
currentLevel = this.NumLevels;
}
}
else
{
changeAmount = (int)Math.Round(1.0 + _rand.NextDouble() * (currentLevel - 1));
currentLevel = currentLevel - changeAmount;
if (currentLevel < 1)
{
currentLevel = 1;
}
}
this.Shape.Add(new Tuple<float, int>(currentAngle * (float)Math.PI / 180.0f, currentLevel));
}
public void Render(SKSurface surface, SKImageInfo info)
{
float centerX = CenterX;
float centerY = CenterY;
float minRadius = Radius - Span / 2.0f;
float maxRadius = Radius + Span / 2.0f;
var context = surface.Canvas;
centerX = info.Width * centerX;
centerY = info.Height * centerY;
float rad = (float)Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height) / 2.0f;
minRadius = minRadius * rad;
maxRadius = maxRadius * rad;
List<float> radii = new List<float>();
List<float> oldRadii;
Tuple<float, int> currentItem;
float lastAngle;
float angleDelta;
int currentRadius;
float currentAngle;
for (var i = 0; i < NumLevels + 1; i++)
{
radii.Add(minRadius + (maxRadius - minRadius) * i / (NumLevels));
}
if (!AreCogsOutward)
{
oldRadii = radii;
radii = new List<float>();
for (var j = oldRadii.Count - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
radii.Add(oldRadii[j]);
}
}
context.Save();
context.Translate(centerX, centerY);
context.RotateDegrees(RotationAngle);
context.Translate(-centerX, -centerY);
SKPath path = new SKPath();
SKColor c = SKColor.FromHsl(
BaseHue,
BaseSaturation,
BaseLightness,
(byte)Math.Round(Opacity * 255.0));
SKPaint p = new SKPaint();
p.IsAntialias = true;
p.IsStroke = false;
p.Color = c;
if (!AreCogsOutward)
{
path.MoveTo(radii[0] + centerX, 0 + centerY);
SKRect r = new SKRect(centerX - radii[0], centerY - radii[0], centerX + radii[0], centerY + radii[0]);
path.ArcTo(r, 360, -180, false);
path.ArcTo(r, 180, -180, false);
path.Close();
}
currentRadius = this.Shape[0].Item2;
lastAngle = 0;
path.MoveTo(radii[currentRadius] + centerX, 0 + centerY);
for (var i = 1; i < this.Shape.Count; i++)
{
currentItem = this.Shape[i];
currentAngle = currentItem.Item1;
currentRadius = currentItem.Item2;
angleDelta = currentAngle - lastAngle;
path.LineTo(
(float)(centerX + radii[currentRadius] * Math.Cos(lastAngle)),
(float)(centerY + radii[currentRadius] * Math.Sin(lastAngle)));
SKRect r = new SKRect(
centerX - radii[currentRadius],
centerY - radii[currentRadius],
centerX + radii[currentRadius],
centerY + radii[currentRadius]);
path.ArcTo(r,
(float)(lastAngle * 180.0 / Math.PI),
(float)((currentAngle - lastAngle) * 180.0 / Math.PI), false);
lastAngle = currentAngle;
}
if (AreCogsOutward)
{
path.Close();
path.MoveTo(radii[0] + centerX, 0 + centerY);
SKRect r = new SKRect(centerX - radii[0], centerY - radii[0], centerX + radii[0], centerY + radii[0]);
path.ArcTo(r, 360, -180, false);
path.ArcTo(r, 180, -180, false);
}
path.Close();
context.DrawPath(path, p);
path.Dispose();
p.Dispose();
context.Restore();
}
}
public class IrisRenderer
{
public IrisRenderer()
{
}
private DateTime _lastRender = DateTime.Now;
private bool _forward = true;
private double _progress = 0;
private double _duration = 5000;
private Random _rand = new Random();
private static double Cubic(double p)
{
return p * p * p;
}
public static double CubicEase(double t)
{
if (t < .5)
{
var fastTime = t * 2.0;
return .5 * Cubic(fastTime);
}
var outFastTime = (1.0 - t) * 2.0;
var y = 1.0 - Cubic(outFastTime);
return .5 * y + .5;
}
private bool _first = true;
public void RenderIris(SKSurface surface, SKImageInfo info)
{
if (_first)
{
_first = false;
_lastRender = DateTime.Now;
}
var currTime = DateTime.Now;
var elapsed = (currTime - _lastRender).TotalMilliseconds;
_lastRender = currTime;
if (_forward)
{
_progress += elapsed / _duration;
}
else
{
_progress -= elapsed / _duration;
}
if (_progress > 1.0)
{
_progress = 1.0;
_forward = false;
_duration = 1000 + 4000 * _rand.NextDouble();
}
if (_progress < 0)
{
_progress = 0;
_forward = true;
_duration = 1000 + 4000 * _rand.NextDouble();
}
var context = surface.Canvas;
context.DrawColor(SKColors.Transparent, SKBlendMode.Clear);
//Determine the center for the circle.
var centerX = info.Width / 2.0f;
var centerY = info.Height / 2.0f;
//Determine the radius for the circle.
var rad = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height) / 2.0f;
var fromR = 255;
var fromG = 0;
var fromB = 0;
var toR = 0;
var toG = 0;
var toB = 255;
var actualProgress = CubicEase(_progress);
var actualR = (byte)Math.Round(fromR + (double)(toR - fromR) * actualProgress);
var actualG = (byte)Math.Round(fromG + (double)(toG - fromG) * actualProgress);
var actualB = (byte)Math.Round(fromB + (double)(toB - fromB) * actualProgress);
//Create the paint object to fill the circle.
using (SKPaint p = new SKPaint())
{
p.IsStroke = false;
p.IsAntialias = true;
p.Color = new SKColor(actualR, actualG, actualB);
//Fill the circle.
context.DrawCircle(centerX, centerY, rad, p);
};
}
}
}
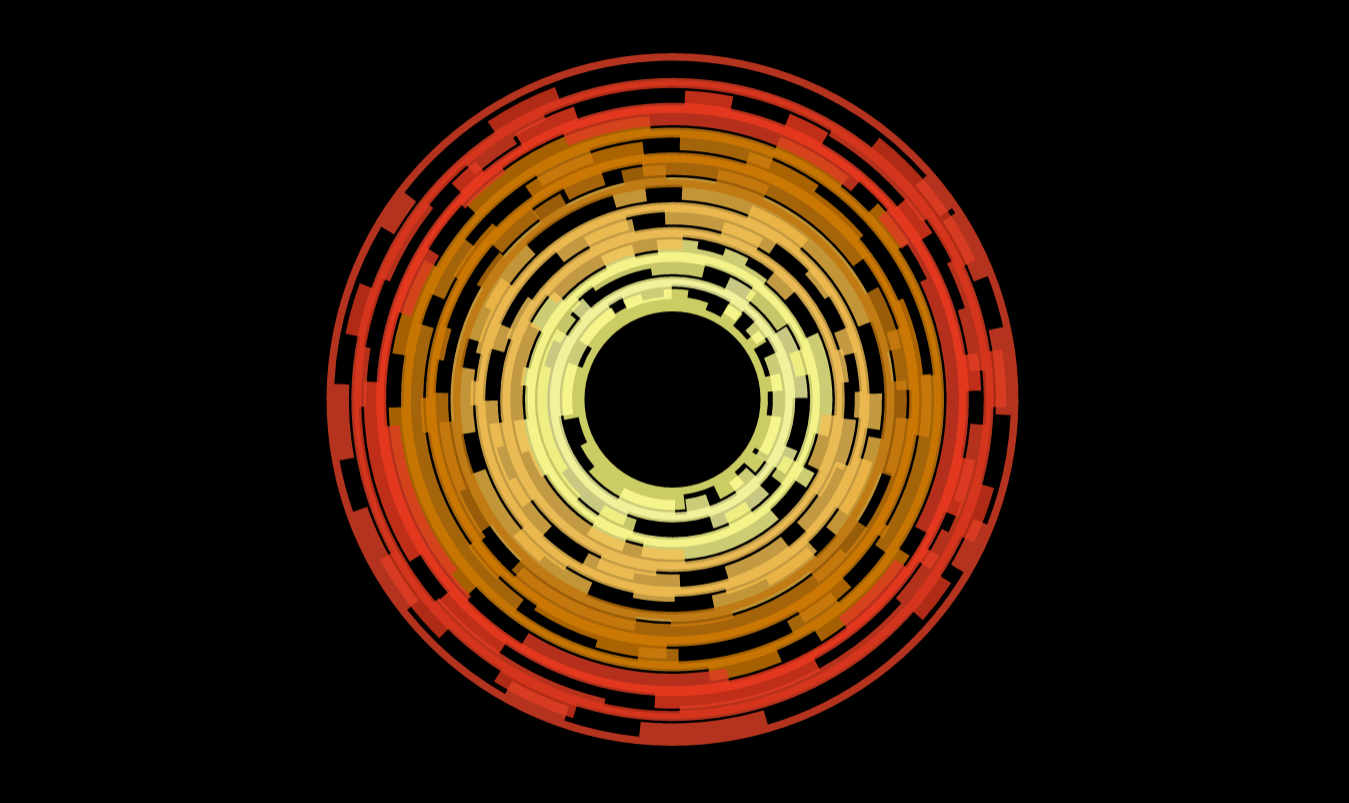
이 기사의 이 논리에서 무슨 일이 일어나고 있는지에 대해서는 자세히 설명하지 않겠지만, 관심이 있다면 다음 기사에서 자세히 설명할 수 있습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 저는 여러 플랫폼에서 많은 복잡한 logic 를 재사용할 수 있는 방법을 보여주는 방식으로 이것을 제시합니다. 지금 앱을 다시 실행하면 서로 맞물리는 톱니바퀴 카운터가 서로 반대 회전하는 복잡한 시각적 개체를 볼 수 있습니다.

그리고 여기 움직이는 비디오입니다.
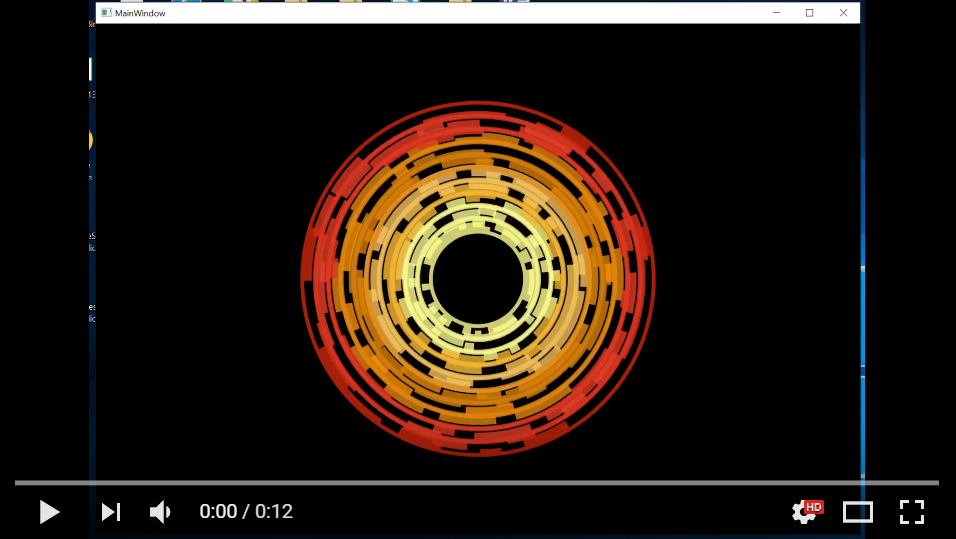
이제 이것이 굉장 하다고 믿습니까? 그 결과, "그레이엄, SkiaSharp을 사용하면 여러 플랫폼에서 고성능 렌더링을 쉽게 수행할 수 있다면 누군가 크로스 플랫폼 앱에서 사용할 수 있는 정말 멋진 UI를 만들면 깔끔하지 않을까요?"라고 생각할 수 있습니다. 글쎄요, 네, 사실, 그것이 우리가 정확히 그렇게 한 이유입니다.
마무리
한동안 Infragistics + Xamarin를 팔로우 해 왔다면 한동안 Xamarin 기반 제품이 있었다는 것을 알 수 있습니다 (그리고 지금 새 버전이 나왔다는 것을 알 수 있습니다!). 그러나 명확하지 않을 수 있는 것은 제품의 새 버전이 17.0 릴리스의 모든 플랫폼 간에 완전히 일관된 API, 성능 및 동작 스토리를 갖도록 크게 재설계되었다는 것입니다. Xamarin 제품의 이전 버전은 기본 Android 및 iOS 제품에 비해 얇은 베니어였습니다. 이것은 우리의 기본 모바일 API가 서로 충분히 유사했기 때문에 가능했습니다. 그러나 일관성을 극대화하기 위한 측면에서 API는 서로 충분히 일관성이 없었고(일부 구성 요소의 경우 완전히 분산됨) 이 전략은 원하는 것보다 더 비싸고 제한적이었습니다. 그리고 우리는 .NET 기반 데이터를 (확실히 non-.NET) 기본 구성 요소에 대해 효율적으로 직접 바인딩할 수 있도록 내부적으로 엄청난 흑마법을 부렸지만, 이 작업은 무대 뒤에서 엄청나게 복잡했습니다.
SkiaSharp이 등장했을 때 렌더링 계층까지 "끝까지" 제품을 C# 제품으로 다시 구상하고 API(및 기본 논리)를 Xamarin 간에 가능한 한 동일하게 다시 초점을 맞출 수 있는 기회가 있다는 것을 알았습니다. 양식, Xamarin. Android, Xamarin.iOS 및 데스크톱 XAML 플랫폼과 매우 유사합니다. 데스크톱에 몇 가지 고유한 WPF 기능이 있다는 사실을 제외하고, 우리는 보편적으로 모든 것을 매우 가깝게 만들었으므로 많은 경우 사소한 조정만 또는 전혀 조정하지 않고 플랫폼 간에 로직을 붙여넣을 수 있습니다. 무엇보다도 새로운 Xamarin 구성 요소를 사용할 때 대부분의 경우 인기 있는 데스크톱 WPF 제품에서와 동일한 논리를 실행하게 됩니다. 우리는 우리가 한 일을 매우 자랑스럽게 생각하며 그것이 당신을 기쁘게 하기를 바랍니다! 저희에게 알려주세요!
-Graham